Interested in growing your wealth and achieving financial freedom, but intimidated by the complexities of the stock market? You’re not alone. Many people perceive investing as a risky game reserved for financial experts. The truth is, investing in the stock market is an accessible and effective way to build long-term wealth, even for beginners. This guide will demystify the process, providing you with the knowledge and tools to start investing safely and confidently.
We’ll cover everything from understanding basic investment terminology and choosing the right investment accounts to researching stocks, evaluating risks, and diversifying your portfolio. Our goal is to empower you to make informed decisions, avoid common pitfalls, and embark on your investment journey with the foundation needed for success.
Why Invest in the Stock Market?
Investing in the stock market is one of the most effective ways to build wealth over time. While it carries risk, the potential rewards are significant. Here’s why you should consider investing:
Grow Your Wealth: Historically, the stock market has delivered higher returns than traditional savings accounts or bonds. By investing in stocks, you’re buying a piece of companies you believe in, participating in their growth and potentially earning substantial returns.
Outpace Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your money over time. Stock market investments have the potential to outpace inflation, helping you maintain your standard of living and grow your wealth even during periods of rising prices.
Reach Financial Goals: Whether it’s buying a house, funding your retirement, or securing your children’s education, investing in the stock market can be a powerful tool to achieve your long-term financial goals. By starting early and investing consistently, you can harness the power of compounding to accelerate your progress.
Understanding Stock Market Basics

The stock market can seem like a complicated system, but at its core, it’s simply a marketplace. Just like a traditional market where goods are bought and sold, the stock market facilitates the buying and selling of pieces of companies, known as stocks or shares.
When you buy a share of stock, you’re essentially becoming a part-owner of that company. The more shares you own, the larger your ownership stake. As a shareholder, you have the potential to profit from the company’s success in two primary ways:
- Dividends: Companies may distribute a portion of their profits to shareholders in the form of dividends.
- Stock Price Appreciation: If a company performs well, demand for its stock typically increases, driving up the stock’s price. You can then sell your shares for a profit.
The stock market is influenced by a multitude of factors, including company performance, economic indicators, and investor sentiment. This interplay of factors contributes to the stock market’s characteristic volatility, meaning prices can fluctuate significantly in the short term.
How to Choose the Right Stocks for Beginners
Navigating the stock market can feel like entering a maze, especially for beginners. Choosing the right stocks is crucial for a successful investing journey. Here’s a simplified approach:
1. Start with What You Know: Invest in industries and companies familiar to you. Understanding a business’s products, services, and target market provides valuable insight into its potential for growth.
2. Research and Analyze: Don’t rely solely on hype. Conduct thorough research on potential companies. Examine their financial statements, understand their competitive landscape, and assess their future prospects.
3. Consider ETFs and Mutual Funds: Exchange-Traded Funds (ETFs) and mutual funds offer instant diversification by pooling money from multiple investors to invest in a basket of assets. This spreads risk and can be less volatile than individual stocks.
4. Think Long-Term: Avoid trying to “get rich quick.” Focus on long-term growth potential. Look for companies with a solid track record, strong management, and a sustainable competitive advantage.
5. Start Small and Diversify: Begin with a manageable investment amount and diversify your portfolio across different industries and sectors. This minimizes risk by ensuring that one poorly performing stock won’t significantly impact your entire portfolio.
Diversifying Your Investment Portfolio
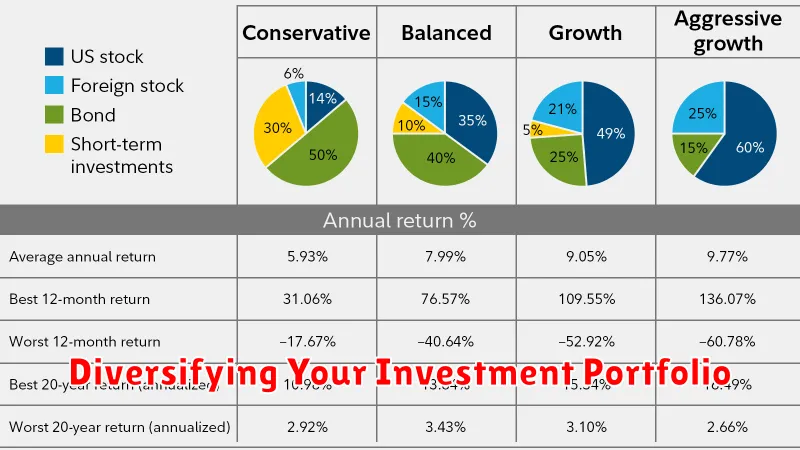
Diversification is a key element of safe and strategic investing. Essentially, it means not putting all your eggs in one basket. Instead of investing heavily in a single company, sector, or asset class, you spread your risk by investing in a variety.
Why is this important? If one of your investments performs poorly, the others can help cushion the blow. For example, if you hold only tech stocks and the tech sector experiences a downturn, your entire portfolio will suffer. However, if you also own stocks in healthcare, consumer goods, and bonds, the losses in tech are balanced by the potential for gains in other areas.
How to Diversify:
- Across asset classes: Invest in a mix of stocks, bonds, real estate, and potentially commodities.
- Within asset classes: Don’t just buy large-cap stocks; diversify into small-cap and mid-cap stocks as well.
- Across sectors: Hold stocks from various sectors like technology, healthcare, financials, and energy.
- Geographically: Consider international stocks or funds to gain exposure to different markets.
Remember, diversification doesn’t guarantee profits or eliminate risk, but it does help mitigate potential losses and can lead to more stable returns over the long term. As you gain more investing experience, you can refine your diversification strategy to align with your risk tolerance and financial goals.
Risks Involved in Stock Market Investing
Investing in the stock market offers the potential for growth, but it is essential to understand the inherent risks involved. Here are some key risks to consider:
Market Risk: Stock prices can fluctuate significantly due to factors such as economic conditions, interest rates, and investor sentiment. This volatility can lead to both profits and losses, and it’s impossible to predict market movements with certainty.
Company-Specific Risk: The performance of individual companies can impact the value of their stock. Factors such as poor management, competition, and changing industry trends can all negatively affect a company’s stock price.
Inflation Risk: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of money over time. While some companies can pass along rising costs to consumers, others may struggle, potentially impacting their stock value.
Interest Rate Risk: Changes in interest rates can influence stock prices. Rising rates can make bonds more attractive to investors, potentially leading to a shift of funds away from stocks.
Liquidity Risk: While major stocks are generally easy to buy and sell, some investments, like small-company stocks, may have lower trading volumes, making it harder to exit a position quickly at a desirable price.
Long-Term vs Short-Term Investment Strategies
When venturing into the stock market, one of the fundamental decisions you’ll face is choosing between long-term and short-term investment strategies. Both approaches come with their own set of advantages and disadvantages, catering to different financial goals and risk tolerances.
Long-term investing typically involves holding onto investments for several years, if not decades. This strategy is often associated with a buy-and-hold approach, riding out market fluctuations to benefit from the power of compounding and long-term growth. It’s considered less risky than short-term trading, as it focuses on the underlying fundamentals of a company rather than short-term market sentiment.
Short-term investing, on the other hand, involves capitalizing on short-term market movements by buying and selling assets within a shorter time frame, which could be days, weeks, or months. This approach requires active monitoring of the market and a higher risk tolerance, as it aims to profit from price volatility. While potentially rewarding, it demands significant time, knowledge, and emotional discipline, making it less suitable for beginners.
Ultimately, the best investment strategy for you will depend on your individual circumstances, financial goals, risk tolerance, and time horizon. Before diving in, carefully consider your options, do your research, and if needed, seek advice from a qualified financial advisor.
Tools to Help You Get Started with Stock Investing
Jumping into stock investing can feel overwhelming, but the right tools can make it manageable and even enjoyable. Here’s a look at some essentials:
1. Online Brokerages: These are your gateways to the stock market. They provide platforms to research stocks, place trades, and manage your portfolio. Popular options known for their user-friendly interfaces and resources include Fidelity, Schwab, and TD Ameritrade.
2. Stock Simulators: Before risking real money, practice with virtual trading! Simulators let you experiment with different investment strategies and get comfortable with market mechanics without financial consequences.
3. Research and Analysis Websites/Apps: Knowledge is power in investing. Sites like Yahoo Finance, Google Finance, and Bloomberg offer free real-time quotes, company news, and basic charting tools. For more in-depth analysis and professional insights, consider subscribing to platforms like Morningstar or Seeking Alpha.
4. Financial Education Resources: Investing is a lifelong learning journey. Take advantage of free courses, webinars, and articles offered by reputable sources like Investopedia, Khan Academy, and The Motley Fool to build a solid foundation of financial literacy.
Remember, the best tools are the ones you use consistently. Choose tools that match your learning style, risk tolerance, and investment goals. Don’t be afraid to explore and experiment until you find the perfect fit for your investing journey.

